 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
Yeah, it's dangerous for a community to tolerate and adopt closed-source software. We should have done a better job pressuring them to license it openly.
The OSM wiki pointed me to Maperitive first, but I wish it pointed me to qgis first. We should probably edit the wiki with a huge warning banner that the code is closed, the app is full of bugs, and that it is not (and can not be) updated.
Edit: I took my own advice and added a big red box to the top of the article warning the user and pointing them to QGIS instead.
Edit 2: Do we have any way to know when the latest version of Maperitive (v2.4.3) was released? Usually I'd check the git repo, but..
Edit 3: stat on the Maperitive-latest.zip file says that it's last modified 2018-02-27 17:25:07, so it's at least 6 years old.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
# Make Vector Topographic Maps (Open Street Map, Maperitive, and Inkscape) #### by Michael Altfield This guide will show you how to [generate vector-based **topopgraphic maps**](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/), for printing very large & **high-quality paper wall maps using inkscape**. All of the tools used in this guide are free (as in beer). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | How-to [Guide to Making Vector Topo Maps](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) with Maperitive and Inkscape | # Intro I recently volunteered at a Biological Research Station located on the eastern slopes of the Andes mountains. If the skies were clear (which is almost never, as it\'s a cloud forest), you would have a great view overlooking the Amazon Rainforest below. | [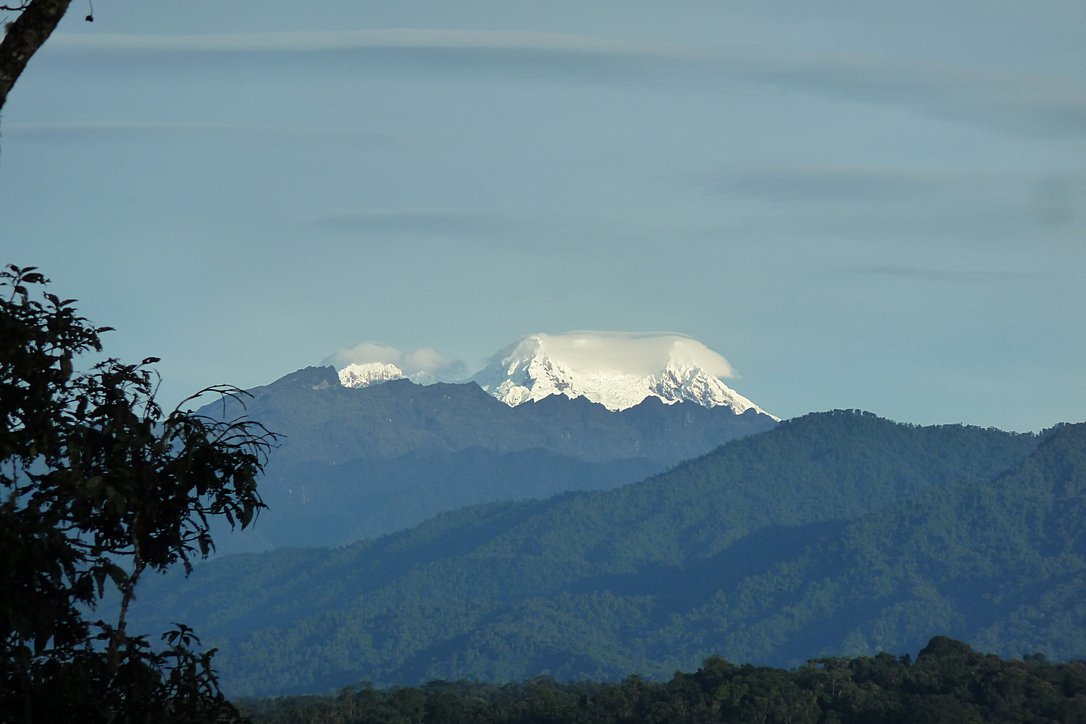](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu is in a cloud forest on the east slopes of the Andes mountains, just 30 km from the summit of the glacial-capped [Antisana](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antisana) volcano ([source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volc%C3%A1n_Antisana_2015-06-14_(9)_(39680659444).jpg)) | The field station was many years old with some permanent structures and a network of established trails that meandered towards the border of Antisana National Park -- a protected area rich with biodiversity that attracts biologists from around the world. At the top of the park is a glacial-capped volcano with a summit at 5,753 meters. Surprisingly, though Estacion Biologicia Yanayacu was over 30 years old, nobody ever prepared a proper map of their trails. And certainly there was no high-resolution topographical map of the area to be found at the Station. That was my task: to **generate maps that we could bring to a local print shop to print-out huge 1-3 meter topographical maps**. And if you want to print massive posters that don\'t look terrible, you\'re going to be working with **vector graphics**. However, most of the tools that I found for browsing Open Street Map data that included contour lines couldn\'t export an SVG. And the tools I found that *could* export an SVG, couldn\'t export contour lines. It took me several days to figure out how to render a topographical map and **export it as an SVG**. This article will explain how, so **you can produce a vector-based topographical map in about half a day** of work. ## Assumptions This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. Debian 12 (bookworm) 2. OsmAnd\~ v4.7.10 3. JOSM v18646 4. Maperitive v2.4.3 5. Inkscape v1.2.2 ## The Tools Unfortunately, there\'s no all-in-one app that will let you just load a slippy map, zoom-in, draw a box, and hit \"export as SVG\". We\'ll be using a few different tools to meet our needs. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) | ### OsmAnd [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) is a mobile app. We\'ll be using OsmAnd to walk around on the trails and generate GPX files (which contain a set of GPS coordinates and some metadata). We\'ll use these coordinates to generate vector lines of a trail overlaying the topographic map. If you just want a topographic map without trails (or your trails are already marked on OSM data), then you won\'t need this tool. In this guide we\'ll be using OsmAnd, but you an also use other apps \-- such as [Organic Maps](https://organicmaps.app/), [Maps.me](https://maps.me/), or [Gaia](https://www.gaiagps.com/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) | ### JOSM [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) is a java-based tool for editing Open Street Map data. We\'ll be using JOSM to upload the paths of our trails (recorded GPX files from OsmAnd) and also to download additional data (rivers, national park boundary line, road to the trailhead, etc). We\'ll then be able to combine all of this data into a larger GPX file, which will eventually become vector lines overlaying the topographic map. You can skip this if you just want contour lines without things like rivers, roads, trails, buildings, and park borders. ### View Finder Panoramas Have you ever wondered how you can zoom-in almost anywhere in the world and see contour lines? I always thought that this was the result of some herculean effort of surveyors scaling mountains and descending canyons the world-over. But, no \-- it\'s a product of the US Space Shuttle program. In the year 2000, an international program called [SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission) was launched into space with the Endaevor Space Shuttle. It consisted of a special radar system tethered to the shuttle with a 60 meter mast as it orbited the earth. | [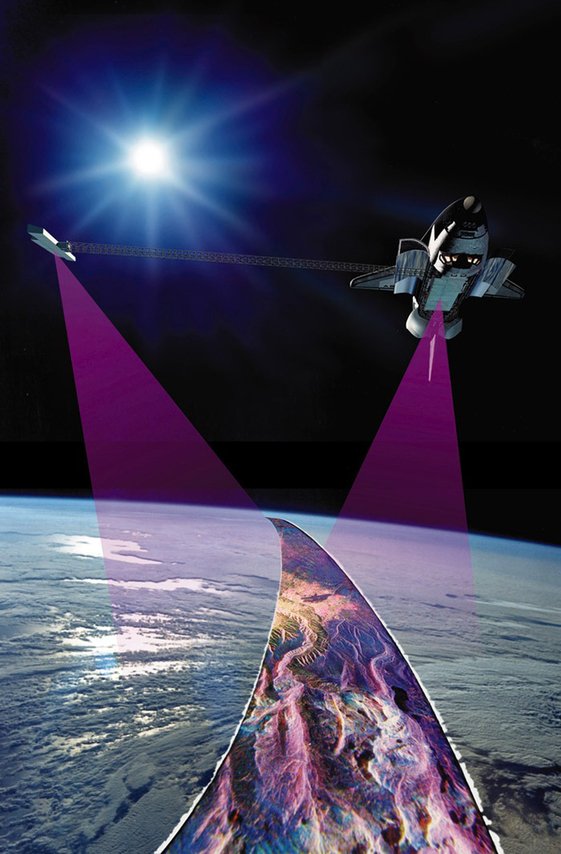](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | This illustration shows the Space Shuttle Endeavour orbiting \~233 kilometers above Earth. The two anternae, one located in the Shuttle bay and the other located on a 60-meter mast, were able to penetrate clouds, obtaining 3-dimentional topographic images of the world\'s surface (source: [NASA](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shuttle_Radar_Topographic_Mission_(SRTM)_Illustration.jpg)) | When the shuttle returned to earth, the majority of our planet\'s contours were mapped. This data was placed on the public domain. Today, it is the main data source for elevation data in most maps. While the data from SRTM was a huge boon to cartographers, it did have some gaps. Namely: elevation data [was missing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission#No-data_areas) in very tall mountains and very low canyons. Subsequent work was done to fill-in these gaps. One particular source that ingested the SRTM data, completed its gaps, and made the results public is Jonathan de Ferranti\'s [viewfinderpanoramas.org](https://viewfinderpanoramas.org/Coverage%20map%20viewfinderpanoramas_org3.htm). We will be downloading [`.hgt`](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/357415/how-to-read-nasa-hgt-binary-files) files from View Finder Panoramas in order to generate vector contour lines for our topographical map. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net/) | ### Maperitive [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net) is a [closed-source](http://maperitive.net/docs/FAQ.html#Where%20is%20the%20source%20code?) .NET-based mapping software (which runs fine in Linux with [mono](https://www.mono-project.com/)). We\'ll be using Maperitive to tie together our GPX tracks, generate contour lines, generate hillshades, and export it all as a SVG. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) | ### Inkscape [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) is a cross-platform app for artists working with vector graphics. We\'ll be using inkscape to make some final touches to our vector image, such as hiding some paths, changing their stroke color/shape/thickness, and adding/moving text labels. Finally, we\'ll use inkscape to export a gigantic, high-definition `.png` raster image (to send to the print shop). # Guide To read the full guide on how to create vector-based maps, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/): * [tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) # Example Maps For example, here\'s the (A4-sized) topo map that I built for Yanayacu. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Final (raster) export, ready for sending to the print shop ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_topo/yanayacu_topo.svg)) | Note that I changed the stroke and thickness of the National Park boundary to be large and green, I changed the path of the road (downloaded from OSM data in JOSM) to be thick and black, and I changed my GPX tracks (recorded in OsmAnd and merged with the OSM data in JOSM) to be thin, dashed, and red. The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) I also used this method to generate a simplified \"trail map\" of Yanayacu (without contour lines). The workflow was similar, except I didn\'t generate contour nor hillshades layers in Maperitive before exporting as a `.svg` | [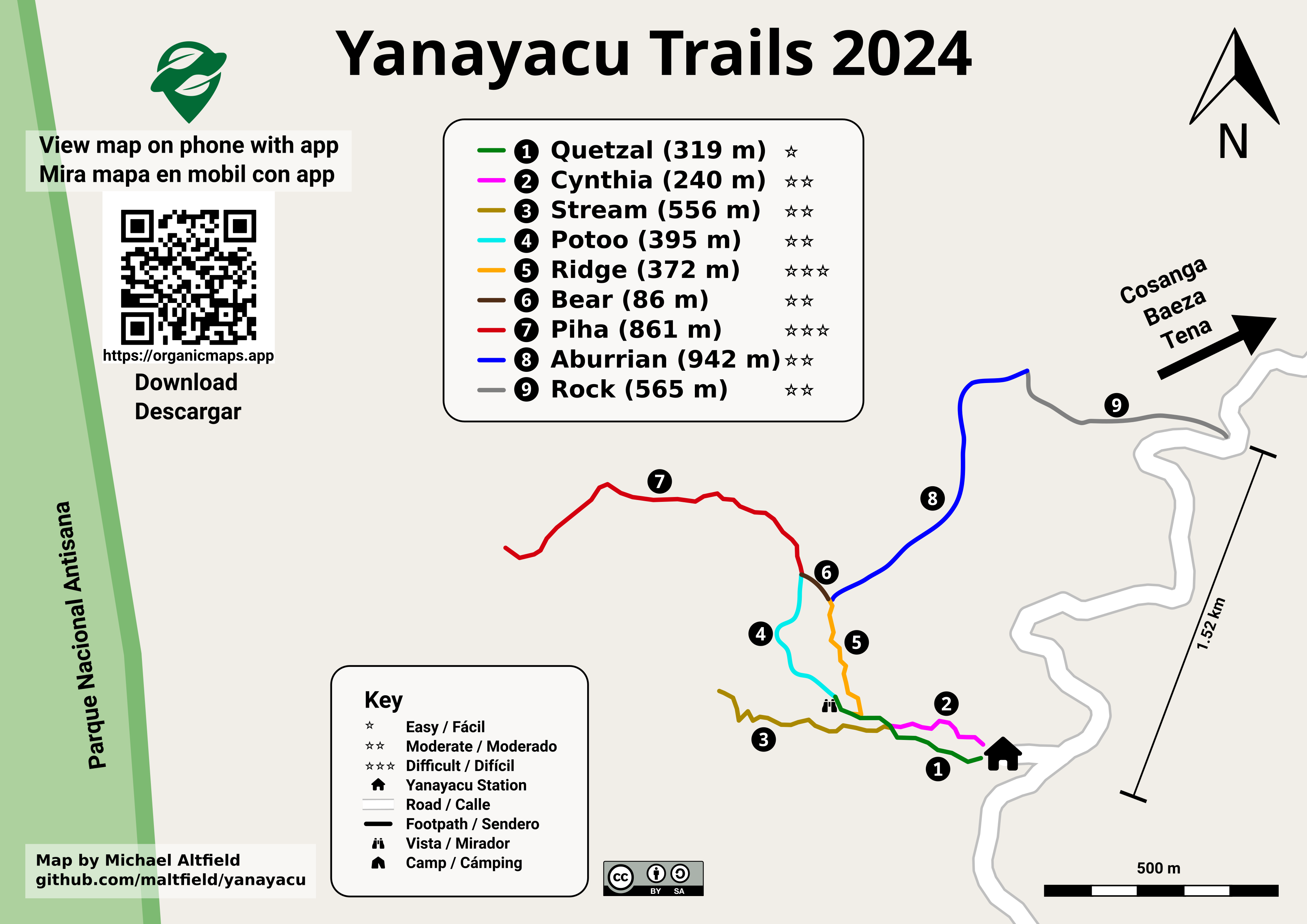)](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu Trail Guide ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide/yanayacu_trail_guide.svg)) | The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide)
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
# Make Vector Topographic Maps (Open Street Map, Maperitive, and Inkscape) #### by Michael Altfield This guide will show you how to [generate vector-based **topopgraphic maps**](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/), for printing very large & **high-quality paper wall maps using inkscape**. All of the tools used in this guide are free (as in beer). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | How-to [Guide to Making Vector Topo Maps](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) with Maperitive and Inkscape | # Intro I recently volunteered at a Biological Research Station located on the eastern slopes of the Andes mountains. If the skies were clear (which is almost never, as it\'s a cloud forest), you would have a great view overlooking the Amazon Rainforest below. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu is in a cloud forest on the east slopes of the Andes mountains, just 30 km from the summit of the glacial-capped [Antisana](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antisana) volcano ([source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volc%C3%A1n_Antisana_2015-06-14_(9)_(39680659444).jpg)) | The field station was many years old with some permanent structures and a network of established trails that meandered towards the border of Antisana National Park -- a protected area rich with biodiversity that attracts biologists from around the world. At the top of the park is a glacial-capped volcano with a summit at 5,753 meters. Surprisingly, though Estacion Biologicia Yanayacu was over 30 years old, nobody ever prepared a proper map of their trails. And certainly there was no high-resolution topographical map of the area to be found at the Station. That was my task: to **generate maps that we could bring to a local print shop to print-out huge 1-3 meter topographical maps**. And if you want to print massive posters that don\'t look terrible, you\'re going to be working with **vector graphics**. However, most of the tools that I found for browsing Open Street Map data that included contour lines couldn\'t export an SVG. And the tools I found that *could* export an SVG, couldn\'t export contour lines. It took me several days to figure out how to render a topographical map and **export it as an SVG**. This article will explain how, so **you can produce a vector-based topographical map in about half a day** of work. ## Assumptions This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. Debian 12 (bookworm) 2. OsmAnd\~ v4.7.10 3. JOSM v18646 4. Maperitive v2.4.3 5. Inkscape v1.2.2 ## The Tools Unfortunately, there\'s no all-in-one app that will let you just load a slippy map, zoom-in, draw a box, and hit \"export as SVG\". We\'ll be using a few different tools to meet our needs. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) | ### OsmAnd [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) is a mobile app. We\'ll be using OsmAnd to walk around on the trails and generate GPX files (which contain a set of GPS coordinates and some metadata). We\'ll use these coordinates to generate vector lines of a trail overlaying the topographic map. If you just want a topographic map without trails (or your trails are already marked on OSM data), then you won\'t need this tool. In this guide we\'ll be using OsmAnd, but you an also use other apps \-- such as [Organic Maps](https://organicmaps.app/), [Maps.me](https://maps.me/), or [Gaia](https://www.gaiagps.com/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) | ### JOSM [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) is a java-based tool for editing Open Street Map data. We\'ll be using JOSM to upload the paths of our trails (recorded GPX files from OsmAnd) and also to download additional data (rivers, national park boundary line, road to the trailhead, etc). We\'ll then be able to combine all of this data into a larger GPX file, which will eventually become vector lines overlaying the topographic map. You can skip this if you just want contour lines without things like rivers, roads, trails, buildings, and park borders. ### View Finder Panoramas Have you ever wondered how you can zoom-in almost anywhere in the world and see contour lines? I always thought that this was the result of some herculean effort of surveyors scaling mountains and descending canyons the world-over. But, no \-- it\'s a product of the US Space Shuttle program. In the year 2000, an international program called [SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission) was launched into space with the Endaevor Space Shuttle. It consisted of a special radar system tethered to the shuttle with a 60 meter mast as it orbited the earth. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | This illustration shows the Space Shuttle Endeavour orbiting \~233 kilometers above Earth. The two anternae, one located in the Shuttle bay and the other located on a 60-meter mast, were able to penetrate clouds, obtaining 3-dimentional topographic images of the world\'s surface (source: [NASA](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shuttle_Radar_Topographic_Mission_(SRTM)_Illustration.jpg)) | When the shuttle returned to earth, the majority of our planet\'s contours were mapped. This data was placed on the public domain. Today, it is the main data source for elevation data in most maps. While the data from SRTM was a huge boon to cartographers, it did have some gaps. Namely: elevation data [was missing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission#No-data_areas) in very tall mountains and very low canyons. Subsequent work was done to fill-in these gaps. One particular source that ingested the SRTM data, completed its gaps, and made the results public is Jonathan de Ferranti\'s [viewfinderpanoramas.org](https://viewfinderpanoramas.org/Coverage%20map%20viewfinderpanoramas_org3.htm). We will be downloading [`.hgt`](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/357415/how-to-read-nasa-hgt-binary-files) files from View Finder Panoramas in order to generate vector contour lines for our topographical map. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net/) | ### Maperitive [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net) is a [closed-source](http://maperitive.net/docs/FAQ.html#Where%20is%20the%20source%20code?) .NET-based mapping software (which runs fine in Linux with [mono](https://www.mono-project.com/)). We\'ll be using Maperitive to tie together our GPX tracks, generate contour lines, generate hillshades, and export it all as a SVG. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) | ### Inkscape [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) is a cross-platform app for artists working with vector graphics. We\'ll be using inkscape to make some final touches to our vector image, such as hiding some paths, changing their stroke color/shape/thickness, and adding/moving text labels. Finally, we\'ll use inkscape to export a gigantic, high-definition `.png` raster image (to send to the print shop). # Guide To read the full guide on how to create vector-based maps, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/): * [tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) # Example Maps For example, here\'s the (A4-sized) topo map that I built for Yanayacu. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Final (raster) export, ready for sending to the print shop ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_topo/yanayacu_topo.svg)) | Note that I changed the stroke and thickness of the National Park boundary to be large and green, I changed the path of the road (downloaded from OSM data in JOSM) to be thick and black, and I changed my GPX tracks (recorded in OsmAnd and merged with the OSM data in JOSM) to be thin, dashed, and red. The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) I also used this method to generate a simplified \"trail map\" of Yanayacu (without contour lines). The workflow was similar, except I didn\'t generate contour nor hillshades layers in Maperitive before exporting as a `.svg` | [)](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu Trail Guide ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide/yanayacu_trail_guide.svg)) | The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide)
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
# Make Vector Topographic Maps (Open Street Map, Maperitive, and Inkscape) #### by Michael Altfield This guide will show you how to [generate vector-based **topopgraphic maps**](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/), for printing very large & **high-quality paper wall maps using inkscape**. All of the tools used in this guide are free (as in beer). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | How-to [Guide to Making Vector Topo Maps](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) with Maperitive and Inkscape | # Intro I recently volunteered at a Biological Research Station located on the eastern slopes of the Andes mountains. If the skies were clear (which is almost never, as it\'s a cloud forest), you would have a great view overlooking the Amazon Rainforest below. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu is in a cloud forest on the east slopes of the Andes mountains, just 30 km from the summit of the glacial-capped [Antisana](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antisana) volcano ([source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volc%C3%A1n_Antisana_2015-06-14_(9)_(39680659444).jpg)) | The field station was many years old with some permanent structures and a network of established trails that meandered towards the border of Antisana National Park -- a protected area rich with biodiversity that attracts biologists from around the world. At the top of the park is a glacial-capped volcano with a summit at 5,753 meters. Surprisingly, though Estacion Biologicia Yanayacu was over 30 years old, nobody ever prepared a proper map of their trails. And certainly there was no high-resolution topographical map of the area to be found at the Station. That was my task: to **generate maps that we could bring to a local print shop to print-out huge 1-3 meter topographical maps**. And if you want to print massive posters that don\'t look terrible, you\'re going to be working with **vector graphics**. However, most of the tools that I found for browsing Open Street Map data that included contour lines couldn\'t export an SVG. And the tools I found that *could* export an SVG, couldn\'t export contour lines. It took me several days to figure out how to render a topographical map and **export it as an SVG**. This article will explain how, so **you can produce a vector-based topographical map in about half a day** of work. ## Assumptions This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. Debian 12 (bookworm) 2. OsmAnd\~ v4.7.10 3. JOSM v18646 4. Maperitive v2.4.3 5. Inkscape v1.2.2 ## The Tools Unfortunately, there\'s no all-in-one app that will let you just load a slippy map, zoom-in, draw a box, and hit \"export as SVG\". We\'ll be using a few different tools to meet our needs. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) | ### OsmAnd [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) is a mobile app. We\'ll be using OsmAnd to walk around on the trails and generate GPX files (which contain a set of GPS coordinates and some metadata). We\'ll use these coordinates to generate vector lines of a trail overlaying the topographic map. If you just want a topographic map without trails (or your trails are already marked on OSM data), then you won\'t need this tool. In this guide we\'ll be using OsmAnd, but you an also use other apps \-- such as [Organic Maps](https://organicmaps.app/), [Maps.me](https://maps.me/), or [Gaia](https://www.gaiagps.com/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) | ### JOSM [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) is a java-based tool for editing Open Street Map data. We\'ll be using JOSM to upload the paths of our trails (recorded GPX files from OsmAnd) and also to download additional data (rivers, national park boundary line, road to the trailhead, etc). We\'ll then be able to combine all of this data into a larger GPX file, which will eventually become vector lines overlaying the topographic map. You can skip this if you just want contour lines without things like rivers, roads, trails, buildings, and park borders. ### View Finder Panoramas Have you ever wondered how you can zoom-in almost anywhere in the world and see contour lines? I always thought that this was the result of some herculean effort of surveyors scaling mountains and descending canyons the world-over. But, no \-- it\'s a product of the US Space Shuttle program. In the year 2000, an international program called [SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission) was launched into space with the Endaevor Space Shuttle. It consisted of a special radar system tethered to the shuttle with a 60 meter mast as it orbited the earth. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | This illustration shows the Space Shuttle Endeavour orbiting \~233 kilometers above Earth. The two anternae, one located in the Shuttle bay and the other located on a 60-meter mast, were able to penetrate clouds, obtaining 3-dimentional topographic images of the world\'s surface (source: [NASA](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shuttle_Radar_Topographic_Mission_(SRTM)_Illustration.jpg)) | When the shuttle returned to earth, the majority of our planet\'s contours were mapped. This data was placed on the public domain. Today, it is the main data source for elevation data in most maps. While the data from SRTM was a huge boon to cartographers, it did have some gaps. Namely: elevation data [was missing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission#No-data_areas) in very tall mountains and very low canyons. Subsequent work was done to fill-in these gaps. One particular source that ingested the SRTM data, completed its gaps, and made the results public is Jonathan de Ferranti\'s [viewfinderpanoramas.org](https://viewfinderpanoramas.org/Coverage%20map%20viewfinderpanoramas_org3.htm). We will be downloading [`.hgt`](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/357415/how-to-read-nasa-hgt-binary-files) files from View Finder Panoramas in order to generate vector contour lines for our topographical map. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net/) | ### Maperitive [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net) is a [closed-source](http://maperitive.net/docs/FAQ.html#Where%20is%20the%20source%20code?) .NET-based mapping software (which runs fine in Linux with [mono](https://www.mono-project.com/)). We\'ll be using Maperitive to tie together our GPX tracks, generate contour lines, generate hillshades, and export it all as a SVG. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) | ### Inkscape [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) is a cross-platform app for artists working with vector graphics. We\'ll be using inkscape to make some final touches to our vector image, such as hiding some paths, changing their stroke color/shape/thickness, and adding/moving text labels. Finally, we\'ll use inkscape to export a gigantic, high-definition `.png` raster image (to send to the print shop). # Guide To read the full guide on how to create vector-based maps, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/): * [tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) # Example Maps For example, here\'s the (A4-sized) topo map that I built for Yanayacu. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Final (raster) export, ready for sending to the print shop ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_topo/yanayacu_topo.svg)) | Note that I changed the stroke and thickness of the National Park boundary to be large and green, I changed the path of the road (downloaded from OSM data in JOSM) to be thick and black, and I changed my GPX tracks (recorded in OsmAnd and merged with the OSM data in JOSM) to be thin, dashed, and red. The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) I also used this method to generate a simplified \"trail map\" of Yanayacu (without contour lines). The workflow was similar, except I didn\'t generate contour nor hillshades layers in Maperitive before exporting as a `.svg` | [)](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu Trail Guide ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide/yanayacu_trail_guide.svg)) | The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide)
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
# Make Vector Topographic Maps (Open Street Map, Maperitive, and Inkscape) #### by Michael Altfield This guide will show you how to [generate vector-based **topopgraphic maps**](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/), for printing very large & **high-quality paper wall maps using inkscape**. All of the tools used in this guide are free (as in beer). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | How-to [Guide to Making Vector Topo Maps](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) with Maperitive and Inkscape | # Intro I recently volunteered at a Biological Research Station located on the eastern slopes of the Andes mountains. If the skies were clear (which is almost never, as it\'s a cloud forest), you would have a great view overlooking the Amazon Rainforest below. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu is in a cloud forest on the east slopes of the Andes mountains, just 30 km from the summit of the glacial-capped [Antisana](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antisana) volcano ([source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volc%C3%A1n_Antisana_2015-06-14_(9)_(39680659444).jpg)) | The field station was many years old with some permanent structures and a network of established trails that meandered towards the border of Antisana National Park -- a protected area rich with biodiversity that attracts biologists from around the world. At the top of the park is a glacial-capped volcano with a summit at 5,753 meters. Surprisingly, though Estacion Biologicia Yanayacu was over 30 years old, nobody ever prepared a proper map of their trails. And certainly there was no high-resolution topographical map of the area to be found at the Station. That was my task: to **generate maps that we could bring to a local print shop to print-out huge 1-3 meter topographical maps**. And if you want to print massive posters that don\'t look terrible, you\'re going to be working with **vector graphics**. However, most of the tools that I found for browsing Open Street Map data that included contour lines couldn\'t export an SVG. And the tools I found that *could* export an SVG, couldn\'t export contour lines. It took me several days to figure out how to render a topographical map and **export it as an SVG**. This article will explain how, so **you can produce a vector-based topographical map in about half a day** of work. ## Assumptions This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. Debian 12 (bookworm) 2. OsmAnd\~ v4.7.10 3. JOSM v18646 4. Maperitive v2.4.3 5. Inkscape v1.2.2 ## The Tools Unfortunately, there\'s no all-in-one app that will let you just load a slippy map, zoom-in, draw a box, and hit \"export as SVG\". We\'ll be using a few different tools to meet our needs. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) | ### OsmAnd [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) is a mobile app. We\'ll be using OsmAnd to walk around on the trails and generate GPX files (which contain a set of GPS coordinates and some metadata). We\'ll use these coordinates to generate vector lines of a trail overlaying the topographic map. If you just want a topographic map without trails (or your trails are already marked on OSM data), then you won\'t need this tool. In this guide we\'ll be using OsmAnd, but you an also use other apps \-- such as [Organic Maps](https://organicmaps.app/), [Maps.me](https://maps.me/), or [Gaia](https://www.gaiagps.com/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) | ### JOSM [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) is a java-based tool for editing Open Street Map data. We\'ll be using JOSM to upload the paths of our trails (recorded GPX files from OsmAnd) and also to download additional data (rivers, national park boundary line, road to the trailhead, etc). We\'ll then be able to combine all of this data into a larger GPX file, which will eventually become vector lines overlaying the topographic map. You can skip this if you just want contour lines without things like rivers, roads, trails, buildings, and park borders. ### View Finder Panoramas Have you ever wondered how you can zoom-in almost anywhere in the world and see contour lines? I always thought that this was the result of some herculean effort of surveyors scaling mountains and descending canyons the world-over. But, no \-- it\'s a product of the US Space Shuttle program. In the year 2000, an international program called [SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission) was launched into space with the Endaevor Space Shuttle. It consisted of a special radar system tethered to the shuttle with a 60 meter mast as it orbited the earth. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | This illustration shows the Space Shuttle Endeavour orbiting \~233 kilometers above Earth. The two anternae, one located in the Shuttle bay and the other located on a 60-meter mast, were able to penetrate clouds, obtaining 3-dimentional topographic images of the world\'s surface (source: [NASA](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shuttle_Radar_Topographic_Mission_(SRTM)_Illustration.jpg)) | When the shuttle returned to earth, the majority of our planet\'s contours were mapped. This data was placed on the public domain. Today, it is the main data source for elevation data in most maps. While the data from SRTM was a huge boon to cartographers, it did have some gaps. Namely: elevation data [was missing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission#No-data_areas) in very tall mountains and very low canyons. Subsequent work was done to fill-in these gaps. One particular source that ingested the SRTM data, completed its gaps, and made the results public is Jonathan de Ferranti\'s [viewfinderpanoramas.org](https://viewfinderpanoramas.org/Coverage%20map%20viewfinderpanoramas_org3.htm). We will be downloading [`.hgt`](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/357415/how-to-read-nasa-hgt-binary-files) files from View Finder Panoramas in order to generate vector contour lines for our topographical map. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net/) | ### Maperitive [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net) is a [closed-source](http://maperitive.net/docs/FAQ.html#Where%20is%20the%20source%20code?) .NET-based mapping software (which runs fine in Linux with [mono](https://www.mono-project.com/)). We\'ll be using Maperitive to tie together our GPX tracks, generate contour lines, generate hillshades, and export it all as a SVG. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) | ### Inkscape [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) is a cross-platform app for artists working with vector graphics. We\'ll be using inkscape to make some final touches to our vector image, such as hiding some paths, changing their stroke color/shape/thickness, and adding/moving text labels. Finally, we\'ll use inkscape to export a gigantic, high-definition `.png` raster image (to send to the print shop). # Guide To read the full guide on how to create vector-based maps, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/): * [tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) # Example Maps For example, here\'s the (A4-sized) topo map that I built for Yanayacu. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Final (raster) export, ready for sending to the print shop ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_topo/yanayacu_topo.svg)) | Note that I changed the stroke and thickness of the National Park boundary to be large and green, I changed the path of the road (downloaded from OSM data in JOSM) to be thick and black, and I changed my GPX tracks (recorded in OsmAnd and merged with the OSM data in JOSM) to be thin, dashed, and red. The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) I also used this method to generate a simplified \"trail map\" of Yanayacu (without contour lines). The workflow was similar, except I didn\'t generate contour nor hillshades layers in Maperitive before exporting as a `.svg` | [)](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu Trail Guide ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide/yanayacu_trail_guide.svg)) | The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide)
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
# Make Vector Topographic Maps (Open Street Map, Maperitive, and Inkscape) #### by Michael Altfield This guide will show you how to [generate vector-based **topopgraphic maps**](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/), for printing very large & **high-quality paper wall maps using inkscape**. All of the tools used in this guide are free (as in beer). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | How-to [Guide to Making Vector Topo Maps](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) with Maperitive and Inkscape | # Intro I recently volunteered at a Biological Research Station located on the eastern slopes of the Andes mountains. If the skies were clear (which is almost never, as it\'s a cloud forest), you would have a great view overlooking the Amazon Rainforest below. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu is in a cloud forest on the east slopes of the Andes mountains, just 30 km from the summit of the glacial-capped [Antisana](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antisana) volcano ([source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volc%C3%A1n_Antisana_2015-06-14_(9)_(39680659444).jpg)) | The field station was many years old with some permanent structures and a network of established trails that meandered towards the border of Antisana National Park -- a protected area rich with biodiversity that attracts biologists from around the world. At the top of the park is a glacial-capped volcano with a summit at 5,753 meters. Surprisingly, though Estacion Biologicia Yanayacu was over 30 years old, nobody ever prepared a proper map of their trails. And certainly there was no high-resolution topographical map of the area to be found at the Station. That was my task: to **generate maps that we could bring to a local print shop to print-out huge 1-3 meter topographical maps**. And if you want to print massive posters that don\'t look terrible, you\'re going to be working with **vector graphics**. However, most of the tools that I found for browsing Open Street Map data that included contour lines couldn\'t export an SVG. And the tools I found that *could* export an SVG, couldn\'t export contour lines. It took me several days to figure out how to render a topographical map and **export it as an SVG**. This article will explain how, so **you can produce a vector-based topographical map in about half a day** of work. ## Assumptions This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. Debian 12 (bookworm) 2. OsmAnd\~ v4.7.10 3. JOSM v18646 4. Maperitive v2.4.3 5. Inkscape v1.2.2 ## The Tools Unfortunately, there\'s no all-in-one app that will let you just load a slippy map, zoom-in, draw a box, and hit \"export as SVG\". We\'ll be using a few different tools to meet our needs. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) | ### OsmAnd [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) is a mobile app. We\'ll be using OsmAnd to walk around on the trails and generate GPX files (which contain a set of GPS coordinates and some metadata). We\'ll use these coordinates to generate vector lines of a trail overlaying the topographic map. If you just want a topographic map without trails (or your trails are already marked on OSM data), then you won\'t need this tool. In this guide we\'ll be using OsmAnd, but you an also use other apps \-- such as [Organic Maps](https://organicmaps.app/), [Maps.me](https://maps.me/), or [Gaia](https://www.gaiagps.com/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) | ### JOSM [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) is a java-based tool for editing Open Street Map data. We\'ll be using JOSM to upload the paths of our trails (recorded GPX files from OsmAnd) and also to download additional data (rivers, national park boundary line, road to the trailhead, etc). We\'ll then be able to combine all of this data into a larger GPX file, which will eventually become vector lines overlaying the topographic map. You can skip this if you just want contour lines without things like rivers, roads, trails, buildings, and park borders. ### View Finder Panoramas Have you ever wondered how you can zoom-in almost anywhere in the world and see contour lines? I always thought that this was the result of some herculean effort of surveyors scaling mountains and descending canyons the world-over. But, no \-- it\'s a product of the US Space Shuttle program. In the year 2000, an international program called [SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission) was launched into space with the Endaevor Space Shuttle. It consisted of a special radar system tethered to the shuttle with a 60 meter mast as it orbited the earth. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | This illustration shows the Space Shuttle Endeavour orbiting \~233 kilometers above Earth. The two anternae, one located in the Shuttle bay and the other located on a 60-meter mast, were able to penetrate clouds, obtaining 3-dimentional topographic images of the world\'s surface (source: [NASA](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shuttle_Radar_Topographic_Mission_(SRTM)_Illustration.jpg)) | When the shuttle returned to earth, the majority of our planet\'s contours were mapped. This data was placed on the public domain. Today, it is the main data source for elevation data in most maps. While the data from SRTM was a huge boon to cartographers, it did have some gaps. Namely: elevation data [was missing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission#No-data_areas) in very tall mountains and very low canyons. Subsequent work was done to fill-in these gaps. One particular source that ingested the SRTM data, completed its gaps, and made the results public is Jonathan de Ferranti\'s [viewfinderpanoramas.org](https://viewfinderpanoramas.org/Coverage%20map%20viewfinderpanoramas_org3.htm). We will be downloading [`.hgt`](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/357415/how-to-read-nasa-hgt-binary-files) files from View Finder Panoramas in order to generate vector contour lines for our topographical map. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net/) | ### Maperitive [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net) is a [closed-source](http://maperitive.net/docs/FAQ.html#Where%20is%20the%20source%20code?) .NET-based mapping software (which runs fine in Linux with [mono](https://www.mono-project.com/)). We\'ll be using Maperitive to tie together our GPX tracks, generate contour lines, generate hillshades, and export it all as a SVG. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) | ### Inkscape [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) is a cross-platform app for artists working with vector graphics. We\'ll be using inkscape to make some final touches to our vector image, such as hiding some paths, changing their stroke color/shape/thickness, and adding/moving text labels. Finally, we\'ll use inkscape to export a gigantic, high-definition `.png` raster image (to send to the print shop). # Guide To read the full guide on how to create vector-based maps, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/): * [tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) # Example Maps For example, here\'s the (A4-sized) topo map that I built for Yanayacu. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Final (raster) export, ready for sending to the print shop ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_topo/yanayacu_topo.svg)) | Note that I changed the stroke and thickness of the National Park boundary to be large and green, I changed the path of the road (downloaded from OSM data in JOSM) to be thick and black, and I changed my GPX tracks (recorded in OsmAnd and merged with the OSM data in JOSM) to be thin, dashed, and red. The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) I also used this method to generate a simplified \"trail map\" of Yanayacu (without contour lines). The workflow was similar, except I didn\'t generate contour nor hillshades layers in Maperitive before exporting as a `.svg` | [)](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu Trail Guide ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide/yanayacu_trail_guide.svg)) | The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide)
# Make Vector Topographic Maps (Open Street Map, Maperitive, and Inkscape) #### by Michael Altfield This guide will show you how to [generate vector-based **topopgraphic maps**](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/), for printing very large & **high-quality paper wall maps using inkscape**. All of the tools used in this guide are free (as in beer). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | How-to [Guide to Making Vector Topo Maps](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) with Maperitive and Inkscape | # Intro I recently volunteered at a Biological Research Station located on the eastern slopes of the Andes mountains. If the skies were clear (which is almost never, as it\'s a cloud forest), you would have a great view overlooking the Amazon Rainforest below. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu is in a cloud forest on the east slopes of the Andes mountains, just 30 km from the summit of the glacial-capped [Antisana](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antisana) volcano ([source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volc%C3%A1n_Antisana_2015-06-14_(9)_(39680659444).jpg)) | The field station was many years old with some permanent structures and a network of established trails that meandered towards the border of Antisana National Park -- a protected area rich with biodiversity that attracts biologists from around the world. At the top of the park is a glacial-capped volcano with a summit at 5,753 meters. Surprisingly, though Estacion Biologicia Yanayacu was over 30 years old, nobody ever prepared a proper map of their trails. And certainly there was no high-resolution topographical map of the area to be found at the Station. That was my task: to **generate maps that we could bring to a local print shop to print-out huge 1-3 meter topographical maps**. And if you want to print massive posters that don\'t look terrible, you\'re going to be working with **vector graphics**. However, most of the tools that I found for browsing Open Street Map data that included contour lines couldn\'t export an SVG. And the tools I found that *could* export an SVG, couldn\'t export contour lines. It took me several days to figure out how to render a topographical map and **export it as an SVG**. This article will explain how, so **you can produce a vector-based topographical map in about half a day** of work. ## Assumptions This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. Debian 12 (bookworm) 2. OsmAnd\~ v4.7.10 3. JOSM v18646 4. Maperitive v2.4.3 5. Inkscape v1.2.2 ## The Tools Unfortunately, there\'s no all-in-one app that will let you just load a slippy map, zoom-in, draw a box, and hit \"export as SVG\". We\'ll be using a few different tools to meet our needs. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) | ### OsmAnd [OsmAnd](https://osmand.net/) is a mobile app. We\'ll be using OsmAnd to walk around on the trails and generate GPX files (which contain a set of GPS coordinates and some metadata). We\'ll use these coordinates to generate vector lines of a trail overlaying the topographic map. If you just want a topographic map without trails (or your trails are already marked on OSM data), then you won\'t need this tool. In this guide we\'ll be using OsmAnd, but you an also use other apps \-- such as [Organic Maps](https://organicmaps.app/), [Maps.me](https://maps.me/), or [Gaia](https://www.gaiagps.com/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) | ### JOSM [JOSM](https://josm.openstreetmap.de/) is a java-based tool for editing Open Street Map data. We\'ll be using JOSM to upload the paths of our trails (recorded GPX files from OsmAnd) and also to download additional data (rivers, national park boundary line, road to the trailhead, etc). We\'ll then be able to combine all of this data into a larger GPX file, which will eventually become vector lines overlaying the topographic map. You can skip this if you just want contour lines without things like rivers, roads, trails, buildings, and park borders. ### View Finder Panoramas Have you ever wondered how you can zoom-in almost anywhere in the world and see contour lines? I always thought that this was the result of some herculean effort of surveyors scaling mountains and descending canyons the world-over. But, no \-- it\'s a product of the US Space Shuttle program. In the year 2000, an international program called [SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission) was launched into space with the Endaevor Space Shuttle. It consisted of a special radar system tethered to the shuttle with a 60 meter mast as it orbited the earth. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | This illustration shows the Space Shuttle Endeavour orbiting \~233 kilometers above Earth. The two anternae, one located in the Shuttle bay and the other located on a 60-meter mast, were able to penetrate clouds, obtaining 3-dimentional topographic images of the world\'s surface (source: [NASA](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shuttle_Radar_Topographic_Mission_(SRTM)_Illustration.jpg)) | When the shuttle returned to earth, the majority of our planet\'s contours were mapped. This data was placed on the public domain. Today, it is the main data source for elevation data in most maps. While the data from SRTM was a huge boon to cartographers, it did have some gaps. Namely: elevation data [was missing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shuttle_Radar_Topography_Mission#No-data_areas) in very tall mountains and very low canyons. Subsequent work was done to fill-in these gaps. One particular source that ingested the SRTM data, completed its gaps, and made the results public is Jonathan de Ferranti\'s [viewfinderpanoramas.org](https://viewfinderpanoramas.org/Coverage%20map%20viewfinderpanoramas_org3.htm). We will be downloading [`.hgt`](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/357415/how-to-read-nasa-hgt-binary-files) files from View Finder Panoramas in order to generate vector contour lines for our topographical map. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net/) | ### Maperitive [Maperitive](http://maperitive.net) is a [closed-source](http://maperitive.net/docs/FAQ.html#Where%20is%20the%20source%20code?) .NET-based mapping software (which runs fine in Linux with [mono](https://www.mono-project.com/)). We\'ll be using Maperitive to tie together our GPX tracks, generate contour lines, generate hillshades, and export it all as a SVG. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) | ### Inkscape [Inkscape](https://inkscape.org/) is a cross-platform app for artists working with vector graphics. We\'ll be using inkscape to make some final touches to our vector image, such as hiding some paths, changing their stroke color/shape/thickness, and adding/moving text labels. Finally, we\'ll use inkscape to export a gigantic, high-definition `.png` raster image (to send to the print shop). # Guide To read the full guide on how to create vector-based maps, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/): * [tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) # Example Maps For example, here\'s the (A4-sized) topo map that I built for Yanayacu. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Final (raster) export, ready for sending to the print shop ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_topo/yanayacu_topo.svg)) | Note that I changed the stroke and thickness of the National Park boundary to be large and green, I changed the path of the road (downloaded from OSM data in JOSM) to be thick and black, and I changed my GPX tracks (recorded in OsmAnd and merged with the OSM data in JOSM) to be thin, dashed, and red. The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_topo) I also used this method to generate a simplified \"trail map\" of Yanayacu (without contour lines). The workflow was similar, except I didn\'t generate contour nor hillshades layers in Maperitive before exporting as a `.svg` | [)](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/10/01/osm-contours-svg-maperitive/) | |:--:| | Yanayacu Trail Guide ([source svg](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/blob/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide/yanayacu_trail_guide.svg)) | The source `.svg` file for the above image can be found [here](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide) - [github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide](https://github.com/maltfield/yanayacu/tree/main/maps/yanayacu_trail_guide)
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
The Wordpress Activity Pub plugin is on my TODO list. I opened some bug reports with them recently.
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
what happens if I die? what happens if my site goes down? what happens if a site is "protected" by cloudflare (and therefore makes the content inaccessible to at-risk folks)? what happens if a site has an authwall (and therefore is inaccessible to less-privileged folks)?
I think it's important for us to federate content, not just links.
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
it's a lot of work, but basically I copy the html from wordpress into pandoc, convert it to markdown, and then do a lot of cleanup
I didn't copy the whole post here because it's so much work, but I usually do when there's less images and my articles aren't likely to exceed the max char limit :)
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
This article will describe [how to download an image from a (docker) container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Manual [Download of Container Images](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) with wget and curl | # Intro Remember the good `'ol days when you could just download software by visiting a website and click "download"? Even `apt` and `yum` repositories were just simple HTTP servers that you could just `curl` (or `wget`) from. Using the package manager was, of course, more secure and convenient -- but you could always just download packages manually, if you wanted. But **have you ever tried to `curl` an image from a container registry**, such as docker? Well friends, I have tried. And I have the [scars](https://github.com/BusKill/buskill-app/issues/78#issuecomment-1987374445) to prove it. It was a remarkably complex process that took me weeks to figure-out. Lucky you, this article will break it down. ## Examples Specifically, we'll look at how to download files from two OCI registries. 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Terms First, here's some terminology used by OCI 1. OCI - [Open Container Initiative](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#what-oci) 2. blob - A "blob" in the OCI spec just means a file 3. manifest - A "manifest" in the OCI spec means a list of files ## Prerequisites This guide was written in 2024, and it uses the following software and versions: 1. debian 12 (bookworm) 2. curl 7.88.1 3. OCI Distribution Spec v1.1.0 (which, unintuitively, uses the '[/v2/](https://github.com/distribution/distribution/blob/5e75227fb213162564bab74b146300ffed9f0bbd/docs/content/spec/api.md)' endpoint) Of course, you'll need '`curl`' installed. And, to parse json, '`jq`' too. ``` sudo apt-get install curl jq ``` ## What is OCI? OCI stands for Open Container Initiative. OCI was [originally formed](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) in June 2015 for Docker and CoreOS. Today it's a wider, general-purpose (and annoyingly complex) way that many projects host files (that are extremely non-trivial to download). One does not simply download a file from an OCI-complianet container registry. You must: 1. Generate an authentication token for the API 2. Make an API call to the registry, requesting to download a JSON "Manifest" 3. Parse the JSON Manifest to figure out the hash of the file that you want 4. Determine the download URL from the hash 5. Download the file (which might actually be many distinct file "layers") | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | One does not simply [download from a container registry](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | In order to figure out how to make an API call to the registry, you must first read (and understand) the OCI specs [here](https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/). - <https://opencontainers.org/release-notices/overview/> ## OCI APIs OCI maintains three distinct specifications: 1. image spec 2. runtime spec 3. distribution spec ### OCI "Distribution Spec" API To figure out how to download a file from a container registry, we're interested in the "distribution spec". At the time of writing, the latest "distribution spec" can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf): - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/tag/v1.1.0> - <https://github.com/opencontainers/distribution-spec/releases/download/v1.1.0/oci-distribution-spec-v1.1.0.pdf> The above PDF file defines a set of API endpoints that we can use to query, parse, and then figure out how to download a file from a container registry. The table from the above PDF is copied below: | ID | Method | API Endpoint | Success | Failure | |------|----------|------------------------------------|--------|-----------| | end-1 | `GET` | `/v2/` | `200` | `404`/`401` | | end-2 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `200` | `404` | | end-3 | `GET` / `HEAD` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `200` | `404` | | end-4a | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/` | `202` | `404` | | end-4b | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?digest=<digest>` | `201`/`202` | `404`/`400` | | end-5 | `PATCH` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`416` | | end-6 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>?digest=<digest>` | `201` | `404`/`400` | | end-7 | `PUT` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `201` | `404` | | end-8a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list` | `200` | `404` | | end-8b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/tags/list?n=<integer>&last=<integer>` | `200` | `404` | | end-9 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/manifests/<reference>` | `202` | `404`/`400`/`405` | | end-10 | `DELETE` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/<digest>` | `202` | `404`/`405` | | end-11 | `POST` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/?mount=<digest>&from=<other_name>` | `201` | `404` | | end-12a | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-12b | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/referrers/<digest>?artifactType=<artifactType>` | `200` | `404`/`400` | | end-13 | `GET` | `/v2/<name>/blobs/uploads/<reference>` | `204` | `404` | In OCI, files are (cryptically) called "`blobs`". In order to figure out the file that we want to download, we must first reference the list of files (called a "`manifest`"). The above table shows us how we can download a list of files (manifest) and then download the actual file (blob). # Examples Let's look at how to download files from a couple different OCI registries: 1. [Docker Hub](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) 2. [GitHub Packages](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages) ## Docker Hub To see the full example of downloading images from docker hub, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#docker-hub) ## GitHub Packages To see the full example of downloading files from GitHub Packages, [click here](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget#github-packages). # Why? I wrote this article because many, many folks have inquired about how to manually download files from OCI registries on the Internet, but their simple queries are usually returned with a barrage of useless counter-questions: why the heck would you want to do that!?! The answer is varied. Some people need to get files onto a restricted environment. Either their org doesn't grant them permission to install software on the machine, or the system has firewall-restricted internet access -- or doesn't have internet access at all. ## 3TOFU Personally, the reason that I wanted to be able to download files from an OCI registry was for [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/09/03/container-download-curl-wget) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | Unfortunaetly, most apps using OCI registries are *extremely* insecure. Docker, for example, will happily download malicious images. By default, [it doesn't do *any* authenticity verifications](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/238916/how-to-pin-public-root-key-when-downloading-an-image-with-docker-pull-docker-co?noredirect=1&lq=1) on the payloads it downloaded. Even if you manually enable DCT, there's loads of [pending issues](https://github.com/docker/cli/issues/2752) with it. Likewise, the macOS package manager [brew](https://brew.sh/) has this same problem: it will happily download and install malicious code, because it doesn't use cryptography to verify the authenticity of anything that it downloads. This introduces [watering hole vulnerabilities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watering_hole_attack) when developers use brew to install dependencies in their CI pipelines. My solution to this? [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/). And that requires me to be able to download the file (for verification) on three distinct linux VMs using curl or wget. > ⚠ NOTE: 3TOFU is an approach to harm reduction. > > It is not wise to download and run binaries or code whose authenticity you cannot verify using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline. However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you're going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following a [3TOFU procedure](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) may reduce your risk, but it's better to avoid running unauthenticated code if at all possible. ## Registry (ab)use Container registries were created in 2013 to provide a clever & complex solution to a problem: how to package and serve multiple versions of simplified sources to various consumers spanning multiple operating systems and architectures -- while also packaging them into small, discrete "layers". However, if your project is just serving simple files, then the only thing gained by uploading them to a complex system like a container registry is headaches. Why do developers do this? In the case of brew, their free hosing provider (JFrog's Bintray) [shutdown in 2021](https://jfrog.com/blog/into-the-sunset-bintray-jcenter-gocenter-and-chartcenter/). Brew was already hosting their code on GitHub, so I guess someone looked at "GitHub Packages" and [figured it was](https://github.com/orgs/Homebrew/discussions/691) a good (read: free) replacement. Many developers using Container Registries don't need the complexity, but -- well -- they're just using it as a free place for their FOSS project to store some files, man.
 tech.michaelaltfield.net
tech.michaelaltfield.net
# 3TOFU: Verifying Unsigned Releases **By Michael Altfield** License: CC BY-SA 4.0 https://tech.michaelaltfield.net This article introduces the concept of \"3TOFU\" \-- a harm-reduction process when downloading software that cannot be verified cryptographically. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | |:--:| | Verifying Unsigned Releases with [3TOFU](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | > ⚠ NOTE: This article is about harm reduction. > > It is dangerous to download and run binaries (or code) whose authenticity you cannot verify (using a cryptographic signature from a key stored offline). However, sometimes we cannot avoid it. If you\'re going to proceed with running untrusted code, then following the steps outlined in this guide may reduce your risk. # TOFU TOFU stands for [Trust On First Use](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trust_on_first_use). It\'s a ([often abused](https://security.stackexchange.com/a/238912/213165)) concept of downloading a person or org\'s signing key and just blindly trusting it (instead of [verifying it](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_of_trust)). ## 3TOFU 3TOFU is a process where a user downloads something three times at three different locations. If-and-only-if all three downloads are identical, then you trust it. # Why 3TOFU? During the [Crypto Wars](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crypto_Wars) of the 1990s, it was illegal to export cryptography from the United States. In 1996, after intense public pressure and [legal challenges](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bernstein_v._United_States), the government officially permitted export with the 56-bit [DES cipher](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_Encryption_Standard) \-- which was a known-[vulnerable](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_Encryption_Standard#Chronology) cipher. | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | |:--:| | The EFF\'s [Deep Crack](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EFF_DES_cracker) proved DES to be insecure and pushed a switch to 3DES. | But there was a simple way to use insecure DES to make secure messages: **just use it three times**. 3DES (aka \"[Triple DES](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triple_DES)\") is the process encrypting a message using the insecure symmetric block cipher (DES) three times on each block, to produce an actually secure message (from known attacks at the time). 3TOFU (aka \"Triple TOFU\") is the process of downloading a payload using the insecure method (TOFU) three times, to obtain the payload that\'s magnitudes less likely to be maliciously altered. # 3TOFU Process To best mitigate targeted attacks, 3TOFU should be done: 1. On **three distinct days** 2. On **three distinct machines** (or VMs) 3. Exiting from **three distinct countries** 4. Exiting using **three distinct networks** For example, I\'ll usually execute - **TOFU #1/3** in TAILS (via **Tor**) - **TOFU #2/3** in a Debian VM (via **VPN**) - **TOFU #3/3** on my daily laptop (via **ISP**) The possibility of an attacker maliciously modifying something you download over your ISP\'s network are quite high, depending on which country you live-in. The possibility of an attacker maliciously modifying something you download onto a VM with a freshly installed OS over an encrypted VPN connection (routed internationally and exiting from another country) is much less likely, but still possible \-- especially for a [well-funded adversary](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_persistent_threat). The possibility of an attacker maliciously modifying something you download onto a VM running a hardened OS (like [Whonix](https://www.whonix.org/) or [TAILS](https://tails.net/)) using a hardened browser (like [Tor Browser](https://www.torproject.org/download/)) over an anonymizing network (like Tor) is quite unlikely. **The possibility for someone to execute a network attack on all three downloads is very near-zero** \-- especially if the downloads were spread-out over days or weeks. ## 3TOFU bash Script I provide the following bash script as an example snippet that I run for each of the 3TOFUs. ``` REMOTE_FILES="https://tails.net/tails-signing.key" CURL="/usr/bin/curl" WGET="/usr/bin/wget --retry-on-host-error --retry-connrefused" PYTHON="/usr/bin/python3" # in tails, we must torify if [[ "`whoami`" == "amnesia" ]] ; then CURL="/usr/bin/torify ${CURL}" WGET="/usr/bin/torify ${WGET}" PYTHON="/usr/bin/torify ${PYTHON}" fi tmpDir=`mktemp -d` pushd "${tmpDir}" # first get some info about our internet connection ${CURL} -s https://ifconfig.co/country | head -n1 ${CURL} -s https://check.torproject.org | grep Congratulations | head -n1 # and today's date date -u +"%Y-%m-%d" # get the file for file in ${REMOTE_FILES}; do wget ${file} done # checksum date -u +"%Y-%m-%d" sha256sum * # gpg fingerprint gpg --with-fingerprint --with-subkey-fingerprint --keyid-format 0xlong * ``` Here\'s one example execution of the above script (on a debian DispVM, executed with a VPN). ``` /tmp/tmp.xT9HCeTY0y ~ Canada 2024-05-04 --2024-05-04 14:58:54-- https://tails.net/tails-signing.key Resolving tails.net (tails.net)... 204.13.164.63 Connecting to tails.net (tails.net)|204.13.164.63|:443... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 1387192 (1.3M) [application/octet-stream] Saving to: ‘tails-signing.key’ tails-signing.key 100%[===================>] 1.32M 1.26MB/s in 1.1s 2024-05-04 14:58:56 (1.26 MB/s) - ‘tails-signing.key’ saved [1387192/1387192] 2024-05-04 8c641252767dc8815d3453e540142ea143498f8fbd76850066dc134445b3e532 tails-signing.key gpg: WARNING: no command supplied. Trying to guess what you mean ... pub rsa4096/0xDBB802B258ACD84F 2015-01-18 [C] [expires: 2025-01-25] Key fingerprint = A490 D0F4 D311 A415 3E2B B7CA DBB8 02B2 58AC D84F uid Tails developers (offline long-term identity key) <tails@boum.org> uid Tails developers <tails@boum.org> sub rsa4096/0x3C83DCB52F699C56 2015-01-18 [S] [expired: 2018-01-11] sub rsa4096/0x98FEC6BC752A3DB6 2015-01-18 [S] [expired: 2018-01-11] sub rsa4096/0xAA9E014656987A65 2015-01-18 [S] [revoked: 2015-10-29] sub rsa4096/0xAF292B44A0EDAA41 2016-08-30 [S] [expired: 2018-01-11] sub rsa4096/0xD21DAD38AF281C0B 2017-08-28 [S] [expires: 2025-01-25] sub rsa4096/0x3020A7A9C2B72733 2017-08-28 [S] [revoked: 2020-05-29] sub ed25519/0x90B2B4BD7AED235F 2017-08-28 [S] [expires: 2025-01-25] sub rsa4096/0xA8B0F4E45B1B50E2 2018-08-30 [S] [revoked: 2021-10-14] sub rsa4096/0x7BFBD2B902EE13D0 2021-10-14 [S] [expires: 2025-01-25] sub rsa4096/0xE5DBA2E186D5BAFC 2023-10-03 [S] [expires: 2025-01-25] ``` The TOFU output above shows that the release signing key from the TAILS project is a 4096-bit RSA key with a full fingerprint of \"`A490 D0F4 D311 A415 3E2B B7CA DBB8 02B2 58AC D84F`\". The key file itself has a sha256 hash of \"`8c641252767dc8815d3453e540142ea143498f8fbd76850066dc134445b3e532`\". When doing a 3TOFU, save the output of each execution. After collecting output from all 3 executions (intentionally spread-out over 3 days or more), diff the output. If the output of all three TOFUs match, then the confidence of the file\'s authenticity is very high. # Why do 3TOFU? Unfortunately, many developers think that hosting their releases on a server with https is sufficient to protect their users from obtaining a maliciously-modified release. But https won\'t protect you if: 1. Your DNS or publishing infrastructure is compromised ([it happens](https://github.com/cncf/tag-security/tree/main/supply-chain-security/compromises)), or 2. An attacker has just one (subordinate) CA in the user\'s PKI root store ([it happens](https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/234052/where-can-i-find-a-list-of-all-government-agencies-with-cas-in-pki-root-stores)) Generally speaking, publishing infrastructure compromises are detected and resolved within days and MITM attacks using compromised CAs are targeted attacks (to avoid detection). Therefore, a 3TOFU verification should thwart these types of attacks. > ⚠ Note on hashes: Unfortunately, many well-meaning developers erroneously think that cryptographic hashes provide authenticity, but cryptographic hashes do not provide authenticity \-- they provide integrity. > > Integrity checks are useful to detect corrupted data on-download; it does not protect you from maliciously altered data unless those hashes are cryptographically signed with a key whose private key isn\'t stored on the publishing infrastructure. # Improvements There are some things you can do to further improve the confidence of the authenticity of a file you download from the internet. ## Distinct Domains If possible, download your payload from as many distinct domains as possible. An adversary may successfully compromise the publishing infrastructure of a software project, but it\'s far less likely for them to compromise the project website (eg \'`tails.net`\') *and* their forge (eg \'`github.com`\') *and* their mastodon instance (eg \'`mastodon.social`\'). ## Use TAILS | [](https://tech.michaelaltfield.net/2024/08/04/3tofu/) | |:--:| | [TAILS](https://tails.net/) is by far the best OS to use for security-critical situations. | If you are a high-risk target (investigative journalist, activist, or political dissident) then you should definitely use [TAILS](https://tails.net/) for one of your TOFUs. ## Signature Verification It\'s always better to verify the authenticity of a file using cryptographic signatures than with 3TOFU. Unfortunately, some companies like [Microsoft don\'t sign their releases](https://superuser.com/questions/1623134/how-to-cryptographically-verify-the-authenticity-and-integrity-of-microsoft-wind), so the only option to verify the authenticity of something like a Windows `.iso` is with 3TOFU. Still, whenever you encounter some software that is not signed using an offline key, please do us all a favor and [create a bug report](https://github.com/freedomofpress/dangerzone/issues/761) asking the [developer to sign](https://github.com/osTicket/osTicket/issues/5750) their releases with PGP (or minisign or signify or *something*). ## 4TOFU 3TOFU is easy because [Tor is free](https://www.torproject.org/download/) and most people have access to a VPN (corporate or [commercial](https://www.privacyguides.org/en/vpn/) or an [ssh socks proxy](/2015/05/31/tor-vpn-in-tails-to-bypass-tor-blocking/)). But, if you\'d like, you could also add [i2p](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I2P) or some [other proxy network](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_censorship_circumvention#Software) into the mix (and do 4TOFU).
 maltfield
Now
•
66%
maltfield
Now
•
66%
Well, the title was mostly a take from this post:
But I guess I should have said a "PV system"? Or do you have a better name?
 maltfield
Now
•
50%
maltfield
Now
•
50%
We're not looking to be tied to a grid outside the community. Do you have any links to recommended resources to learn more about microgrids and/or community grids?
If it were me and I understand correctly I would probably not tie the systems together.
Well, the loads of the buildings are different, so tieing them together would be very beneficial. For example, one building is a workshop with lots of power tools and heavy machinery and some other buildings (with equal sq meter rooftops) are residential (with less energy requirements)
 maltfield
Now
•
95%
maltfield
Now
•
95%
Hi, Michael Altfield here. I was the sysadmin for OSE from 2017-2020.
Everything OSE does is transparent, so you can just check the OSE websites to see what everyone is currently working-on. OSE contributors log their hours in a worklog called "OSE Dev". There you can quickly see who is working on what.
The above graphs show 4 contributors in the past ~10 weeks (one is me; we had some issues with the apache config recently). There's no direct link, but you can then check the wiki to see people's work logs (just search for the person's name and Log):
- https://wiki.opensourceecology.org/wiki/Marcin_Log
- https://wiki.opensourceecology.org/wiki/Catarina_Log
- https://wiki.opensourceecology.org/wiki/Alexa_Log
- https://wiki.opensourceecology.org/wiki/Maltfield_Log
I also like to look at the MediaWiki "Recent Changes" page to peak at what people are up-to as well:
I told Marcin about Lemmy back in June 2023. Another OSE contributor even created an OSE community on the slrpnk.net instance, but it appears to have been abandoned. I'll email him about this thread to see if he'll bite and publish updates in this community since there's clearly interest :)
Also, shameless plug: I started an org that's very similar in spirit to OSE called Eco-Libre, with a focus on projects to sustainably enfranchise human rights in smaller communities. We're currently accepting volunteers ;)
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
Can you mention this in your article?
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
Personally I wouldn't run a lemmy instance because of this (and also many other concerns)
I recommend [a] letting the lemmy devs know (eg on GitHub) that this issue is preventing you from running a lemmy instance and [b] donating to alternative projects that actually care about data privacy rights.
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
The fines usually are a percent of revenue or millions of Euros, whichever is higher.
So if your revenue is 0 EUR then they can fine you the millions of Euros instead. The point of the “percent of revenue” alternative was for larger corporations that can get fined tens or hundreds of millions of Euros (or, as it happened to Meta, in some cases -- billions of Euros for a single GDPR violation).
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
The fines usually are a percent of revenue or millions of Euros, whichever is higher.
So if your revenue is 0 EUR then they can fine you the millions of Euros instead. The point of the “percent of revenue” alternative was for larger corporations that can get fined tens or hundreds of millions of Euros (or, as it happened to Meta, in some cases -- billions of Euros for a single GDPR violation).
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
That would be true if their instance wasn't federating. If the instance is federating, then it's downloading content from other users, even if the user isn't registered on the instance. And that content is publicly available.
So if someone discovers their content on their instance and sends them a GDPR request (eg Erasure), then they are legally required to process it.
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
It's definitely not impossible to contact all instances; it's a finite list. But we should have a tool to make this easier. Something that can take a given username or post, do a search, find out all the instances that it federated-to, get the contact for all of those instances, and then send-out a formal "GDPR Erasure Request" to all of the relevant admins.
 maltfield
Now
•
66%
maltfield
Now
•
66%
Did you read the article and the feedback that you've received from your other users?
Any FOSS platform has capacity issues. I run my own FOSS projects with zero grant funds and where I'm the only developer. I understand this issue.
What we're talking about here is prioritization. My point is that you should not prioritize "new features" when existing features are a legal, moral, and grave financial risk to your community. And this isn't just "my priority" -- it's clearly been shown that this is the desired priority of your community.
Please prioritize your GDPR issues.
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
Very nice. Unfortunately it doesn't look like Boost is available on F-Droid.
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
Fortunately, in my case, my image was "orphaned" and never actually attached to a post or comment, so it wouldn't have federated.
If the image has already federated then that's a whole next level problem :(
 maltfield
Now
•
66%
maltfield
Now
•
66%
Unfortunately, the Lemmy devs literally said it would take years to fix this issue. If you think this should be a priority for them, please advocate for them to prioritize it on GitHub:
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
Hi, author here.
I didn't expound on eIDs, but I did link to the Estonian solution, which has been around for more than a decade. It has some issues, but I think it's a good baseline that's better than non-cryptographic State auth systems. I'm going to assume you're talking about the US eID system. I haven't looked much at the USA's eID solution, but I wouldn't be surprised if it's terribly designed.
The EU is currently working on an eID system, with the goal to force all Member States to adopt it by 2016. If done wrong, eIDs could be terrible. If done right, it could greatly improve the security & privacy for all. I recommend the Please Identify Yourself! talk at 37c3 about the state of eID legislation as of Dec 2023 (and how to learn from India, who did eID horribly wrong):
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
Hi, unfortunate author here 😅
The issue happened in Jerboa. I opened a few tickets in the Jerboa app's GitHub to address this:
- jerboa #1361: UI for deleting uploaded files
- jerboa #1362: Setting to hide "upload media" button
- jerboa #1363: Add "confirm upload" step to UX
Can you please tell us which Lemmy client apps you use that store the delete token and have a UI to delete uploaded images?
 maltfield
Now
•
100%
maltfield
Now
•
100%
This is a big problem. At the time of writing:
- Users cannot delete their images on Lemmy
- If a user deletes their account, their images don't get deleted
- There is no WUI for admins to delete images on Lemmy
- It is very difficult for admins to find & delete images on Lemmy (via the CLI)
- The Lemmy team didn't bother documenting how admins can delete images on Lemmy
How to purge images in Lemmy
pict-rs is a third-party simple image hosting service that runs along-side Lemmy for instances that allow users to upload media.
At the time of writing, there is no WUI for admins to find and delete images. You have to manually query the pict-rs database and execute an API call from the command-line. Worse: Lemmy has no documentation telling instance admins how to delete images 🤦
For the purposes of this example, let's assume you're trying to delete the following image
https://monero.town/pictrs/image/001665df-3b25-415f-8a59-3d836bb68dd1.webp
There are two API endpoints in pict-rs that can be used to delete an image
Method One: /image/delete/{delete_token}/{alias}
This API call is publicly-accessible, but it first requires you to
obtain the image's `delete_token`
The `delete_token` is first returned by Lemmy when POSTing to the
`/pictrs/image` endpoint
{
"msg":"ok",
"files":[
{
"file":"001665df-3b25-415f-8a59-3d836bb68dd1.webp",
"delete_token":"d88b7f32-a56f-4679-bd93-4f334764d381"
}
]
}
Two pieces of information are returned here:
- file (aka the "alias") is the server filename of the uploaded image
- delete_token is the token needed to delete the image
Of course, if you didn't capture this image's `delete_token` at
upload-time, then you must fetch it from the postgres DB.
First, open a shell on your running postgres container. If you installed
Lemmy with docker compose, use `docker compose ps` to get the
"SERVICE" name of your postgres host, and then enter it with
`docker exec`
docker compose ps --format "table {{.Service}}\t{{.Image}}\t{{.Name}}"
docker compose exec <docker_service_name> /bin/bash
For example:
user@host:/home/user/lemmy# docker compose ps --format "table {{.Service}}\t{{.Image}}\t{{.Name}}"
SERVICE IMAGE NAME
lemmy dessalines/lemmy:0.19.3 lemmy-lemmy-1
lemmy-ui dessalines/lemmy-ui:0.19.3 lemmy-lemmy-ui-1
pictrs docker.io/asonix/pictrs:0.5.4 lemmy-pictrs-1
postfix docker.io/mwader/postfix-relay lemmy-postfix-1
postgres docker.io/postgres:15-alpine lemmy-postgres-1
proxy docker.io/library/nginx lemmy-proxy-1
user@host:/home/user/lemmy#
user@host:/home/user/lemmy# docker compose exec postgres /bin/bash
postgres:/#
Connect to the database as the `lemmy` user
psql -U lemmy
For example
postgres:/# psql -U lemmy
psql (15.5)
Type "help" for help.
lemmy=#
Query for the image by the "alias" (the filename)
select * from image_upload where pictrs_alias = '<image_filename>';
For example
lemmy=# select * from image_upload where pictrs_alias = '001665df-3b25-415f-8a59-3d836bb68dd1.webp';
local_user_id | pictrs_alias | pictrs_delete_token | published
---------------+--------------+---------------------+-----------
1149 | 001665df-3b25-415f-8a59-3d836bb68dd1.webp | d88b7f32-a56f-4679-bd93-4f334764d381 | 2024-02-07 11:10:17.158741+00
(1 row)
lemmy=#
Now, take the `pictrs_delete_token` from the above output, and use
it to delete the image.
The following command should be able to be run on any computer connected to the internet.
curl -i "https://<instance_domain>/pictrs/image/delete/<pictrs_delete_token>/<image_filename>"
For example:
user@disp9140:~$ curl -i "https://monero.town/pictrs/image/delete/d88b7f32-a56f-4679-bd93-4f334764d381/001665df-3b25-415f-8a59-3d836bb68dd1.webp"
HTTP/2 204 No Content
server: nginx
date: Fri, 09 Feb 2024 15:37:48 GMT
vary: Origin, Access-Control-Request-Method, Access-Control-Request-Headers
cache-control: private
referrer-policy: same-origin
x-content-type-options: nosniff
x-frame-options: DENY
x-xss-protection: 1; mode=block
X-Firefox-Spdy: h2
user@disp9140:~$
ⓘ Note: If you get an `
incorrect_login` error, then try [a] logging into the instance in your web browser and then [b] pasting the "https://<instance_domain>/pictrs/image/delete/<pictrs_delete_token>/<image_filename>" URL into your web browser.
The image should be deleted.
Method Two: /internal/purge?alias={alias}
Alternatively, you could execute the deletion directly inside the pictrs
container. This eliminates the need to fetch the `delete_token`.
First, open a shell on your running `pictrs` container. If you
installed Lemmy with docker compose, use `docker compose ps` to get
the "SERVICE" name of your postgres host, and then enter it with
`docker exec`
docker compose ps --format "table {{.Service}}\t{{.Image}}\t{{.Name}}"
docker compose exec <docker_service_name> /bin/sh
For example:
user@host:/home/user/lemmy# docker compose ps --format "table {{.Service}}\t{{.Image}}\t{{.Name}}"
SERVICE IMAGE NAME
lemmy dessalines/lemmy:0.19.3 lemmy-lemmy-1
lemmy-ui dessalines/lemmy-ui:0.19.3 lemmy-lemmy-ui-1
pictrs docker.io/asonix/pictrs:0.5.4 lemmy-pictrs-1
postfix docker.io/mwader/postfix-relay lemmy-postfix-1
postgres docker.io/postgres:15-alpine lemmy-postgres-1
proxy docker.io/library/nginx lemmy-proxy-1
user@host:/home/user/lemmy#
user@host:/home/user/lemmy# docker compose exec pictrs /bin/sh
~ $
Execute the following command inside the `pictrs` container.
wget --server-response --post-data "" --header "X-Api-Token: ${PICTRS__SERVER__API_KEY}" "http://127.0.0.1:8080/internal/purge?alias=<image_filename>"
For example:
~ $ wget --server-response --post-data "" --header "X-Api-Token: ${PICTRS__SERVER__API_KEY}" "http://127.0.0.1:8080/internal/purge?alias=001665df-3b25-415f-8a59-3d836bb68dd1.webp"
Connecting to 127.0.0.1:8080 (127.0.0.1:8080)
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
content-length: 67
connection: close
content-type: application/json
date: Wed, 14 Feb 2024 12:56:24 GMT
saving to 'purge?alias=001665df-3b25-415f-8a59-3d836bb68dd1.webp'
purge?alias=001665df 100% |*****************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************| 67 0:00:00 ETA
'purge?alias=001665df-3b25-415f-8a59-3d836bb68dd1.webp' saved
~ $
ⓘ Note: There's an error in the pict-rs reference documentation. It says you can POST to `/internal/delete`, but that just returns
404 Not Found.
The image should be deleted
Further Reading
Unfortunately, it seems that the Lemmy develoeprs are not taking these moral and legal (GDPR) risks seriously (they said it may take years before they address them), and they threatened to ban me for trying to highlight the severity of this risk, get them to tag GDPR-related bugs, and to prioritize them.
- lemmy #4433: Deleted Account should delete uploaded media (pictures) too
- lemmy #4441: Users unable to delete their images (pictrs API)
- lemmy #4434: Unapproved users cannot delete their accounts/data
- lemmy #3973: Banned users cannot delete their accounts/data
- lemmy #4445: Create an interface for local users to view and remove images
- lemmy-ui #2359: Allow users to delete images they uploaded
- lemmy-ui #2360: Allow admins to view & delete uploaded images
- lemmy-ui #2361: private_message_disclaimer to include user's matrix handle
- jerboa #1361: UI for deleting uploaded files
- jerboa #1362: Setting to hide "upload media" button
- jerboa #1363: Add "confirm upload" step to UX
- lemmy-docs #293: Document image moderation
If GDPR-compliance is important to you on the fediverse, then please provide feedback to the Lemmy developers in the GitHub links above.
Attribution
This comment was copied from the following article: Nightmare on Lemmy Street (A Fediverse GDPR Horror Story)
 |
|---|
| Nightmare on Lemmy Street (A Fediverse GDPR Horror Story) |
